Canada government citizenship test
The Justice System – Canada Citizenship Test Guide
Canada’s justice system ensures that laws are upheld, rights are protected, and disputes are resolved fairly. It is built on the principles of democracy, equality, fairness, independence, and the rule of law. Understanding this system is important for anyone preparing for the Canadian citizenship test.
Canada government citizenship test
1. Rule of Law
The rule of law is a fundamental principle in Canada. It means:
Everyone is equal before the law
No one is above the law, including government officials and police
Laws apply equally to citizens, permanent residents, and newcomers
Purpose: prevents abuse of power, protects freedoms, and supports a fair society.
Canada government citizenship test
2. The Constitution and the Charter
The Constitution
Canada’s highest legal authority
Defines how government operates
Divides powers between federal and provincial governments
Guarantees democratic rights
The Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms (1982)
Protects essential freedoms, including:
Freedom of expression
Freedom of religion
Mobility rights
Legal rights
Equality rights
Importance for citizenship: newcomers learn which rights they enjoy as Canadians.
Canada government citizenship test
3. Types of Laws in Canada
Canada’s legal system is divided into public law and private (civil) law.
Public Law
Covers:
Criminal law
Constitutional matters
Issues involving government
Private (Civil) Law
Covers disputes between individuals or organizations, such as:
Contracts
Property
Business matters
Family issues
Canada government citizenship test
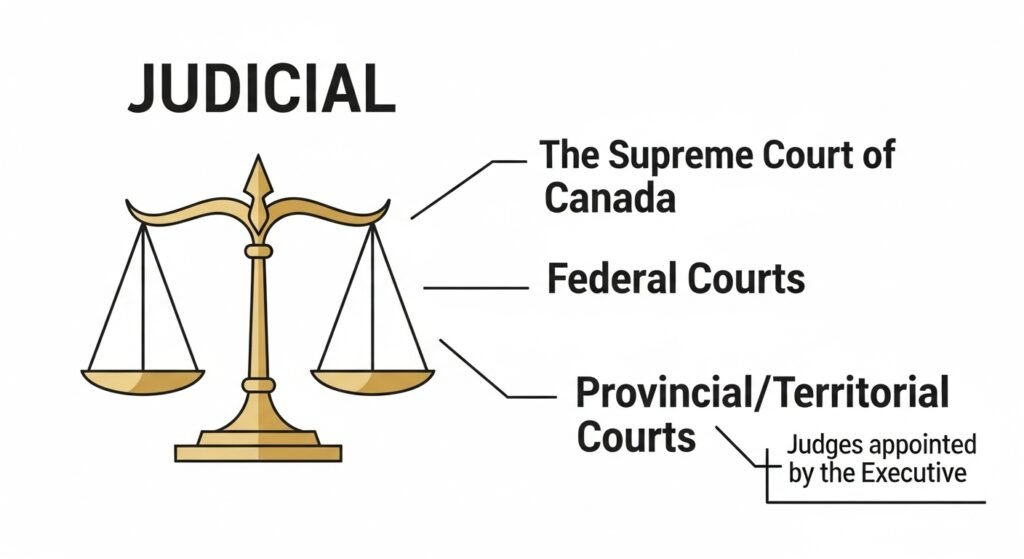
4. The Court System
Canada has a multi-level court system:
Federal Courts
Supreme Court of Canada (highest court)
Federal Court of Appeal
- Tax Court of Canada
Canada government citizenship test
Provincial/Territorial Courts
Handle most:
Criminal cases
Civil disputes
Family law matters
Traffic offences
Small claims
Supreme Court of Canada: the final legal authority in the country; its decisions apply nationwide.
Canada government citizenship test
5. Criminal Justice Process
Canada’s criminal system ensures:
Fair investigations
Presumption of innocence
Right to legal representation
Right to a fair trial
Core Principle: Innocent until proven guilty
Canada government citizenship test
6. Police Services
Police are responsible for maintaining peace, preventing crime, and enforcing laws. Canada has three main levels:
Municipal Police (e.g., Toronto Police Service)
Provincial Police (e.g., OPP, Sûreté du Québec)
Federal Police (RCMP)
The RCMP also serves most territories and some provinces.
Canada government citizenship test
7. Lawyers and Legal Representation
Canadians have the right to hire a lawyer
Courts ensure a fair hearing for all
Legal aid programs provide assistance for those who cannot afford a lawyer (varies by province)
Canada government citizenship test
8. Jury System
Serious criminal trials may use a jury
Jurors are Canadian citizens selected randomly
Jurors must remain impartial and follow the law
Canada government citizenship test
9. Correctional Services and Rehabilitation
Punishments can include:
Prison sentences
Fines
Probation
Community service
Rehabilitation programs
Canada emphasizes rehabilitation and reintegration in addition to punishment.
Canada government citizenship test
10. Responsibilities of Citizens
Citizens help maintain justice by:
Obeying the law
Serving on a jury when required
Respecting the rights of others
These responsibilities are essential for keeping society fair and safe.
Canada government citizenship test